What is Silica
Silica is a group of minerals primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2). It is a term used to describe a variety of minerals that are commonly utilized in the production of lighting fixtures and components. Silica minerals, such as quartz, tridymite, cristobalite, and opal, are abundant in the Earth’s crust, comprising approximately 26 percent of its weight.
Looking For Motion-Activated Energy-Saving Solutions?
Contact us for complete PIR motion sensors, motion-activated energy-saving products, motion sensor switches, and Occupancy/Vacancy commercial solutions.
Silica is valued in the lighting industry for its unique properties, including its high melting point, excellent thermal stability, and transparency to visible light. These characteristics make it suitable for various lighting applications, such as lamp envelopes, lenses, and optical fibers. Additionally, silica can exist in non-crystalline forms, such as vitreous silica or glassy silica, which possess glass-like properties.
While silica minerals are widely used in the lighting industry, the specific applications and uses may vary. Silica’s abundance and desirable properties make it a versatile material for creating lighting components that meet the industry’s requirements for durability, heat resistance, and light transmission.
Maybe You Are Interested In
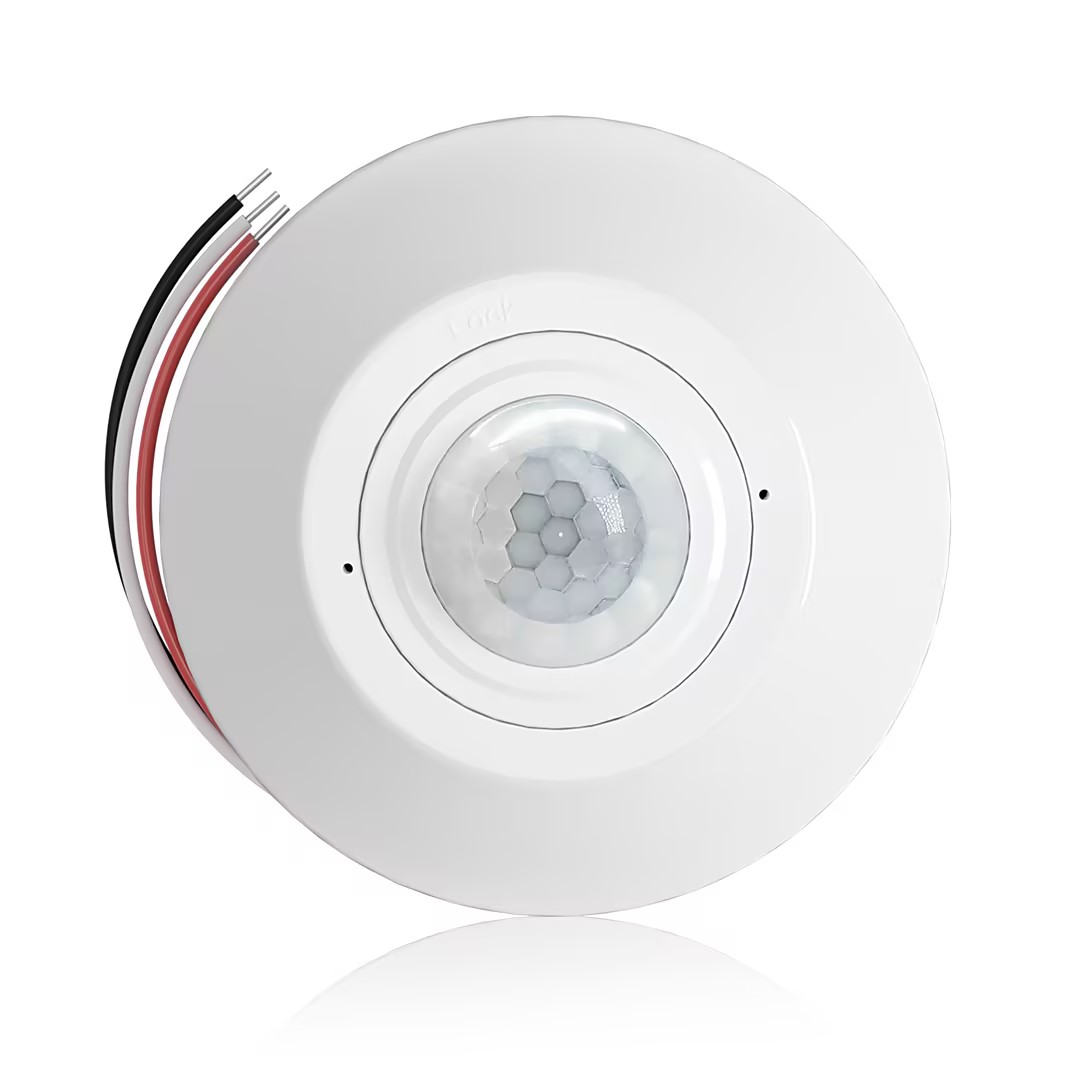
- Occupancy (Auto-ON/Auto-OFF)
- 12–24V DC (10–30VDC), up to 10A
- 360° coverage, 8–12 m diameter
- Time delay 15 s–30 min
- Light sensor Off/15/25/35 Lux
- High/Low sensitivity
- Auto-ON/Auto-OFF occupancy mode
- 100–265V AC, 10A (neutral required)
- 360° coverage; 8–12 m detection diameter
- Time delay 15 s–30 min; Lux OFF/15/25/35; Sensitivity High/Low
- Auto-ON/Auto-OFF occupancy mode
- 100–265V AC, 5A (neutral required)
- 360° coverage; 8–12 m detection diameter
- Time delay 15 s–30 min; Lux OFF/15/25/35; Sensitivity High/Low
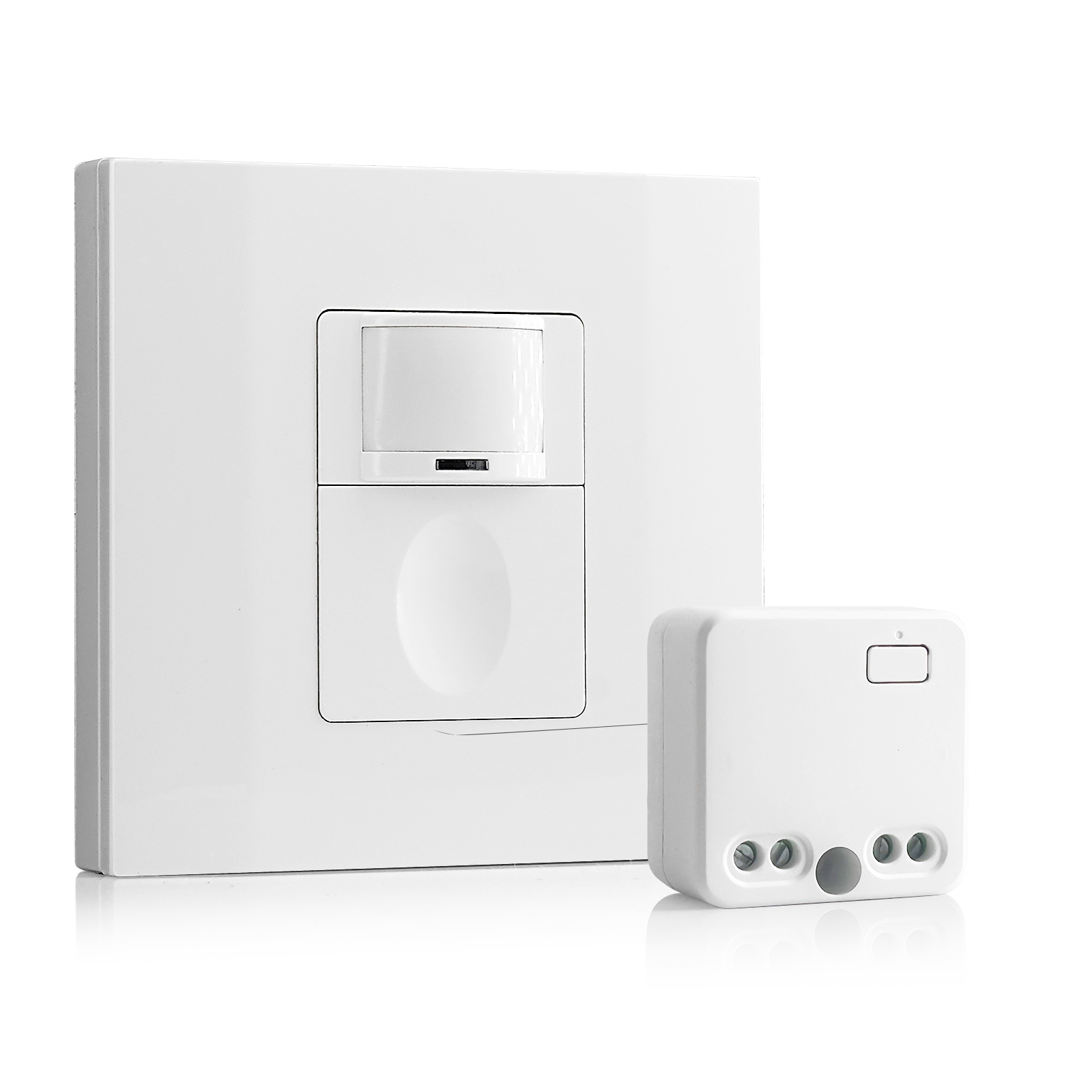
- 100V-230VAC
- Transmission Distance: up to 20m
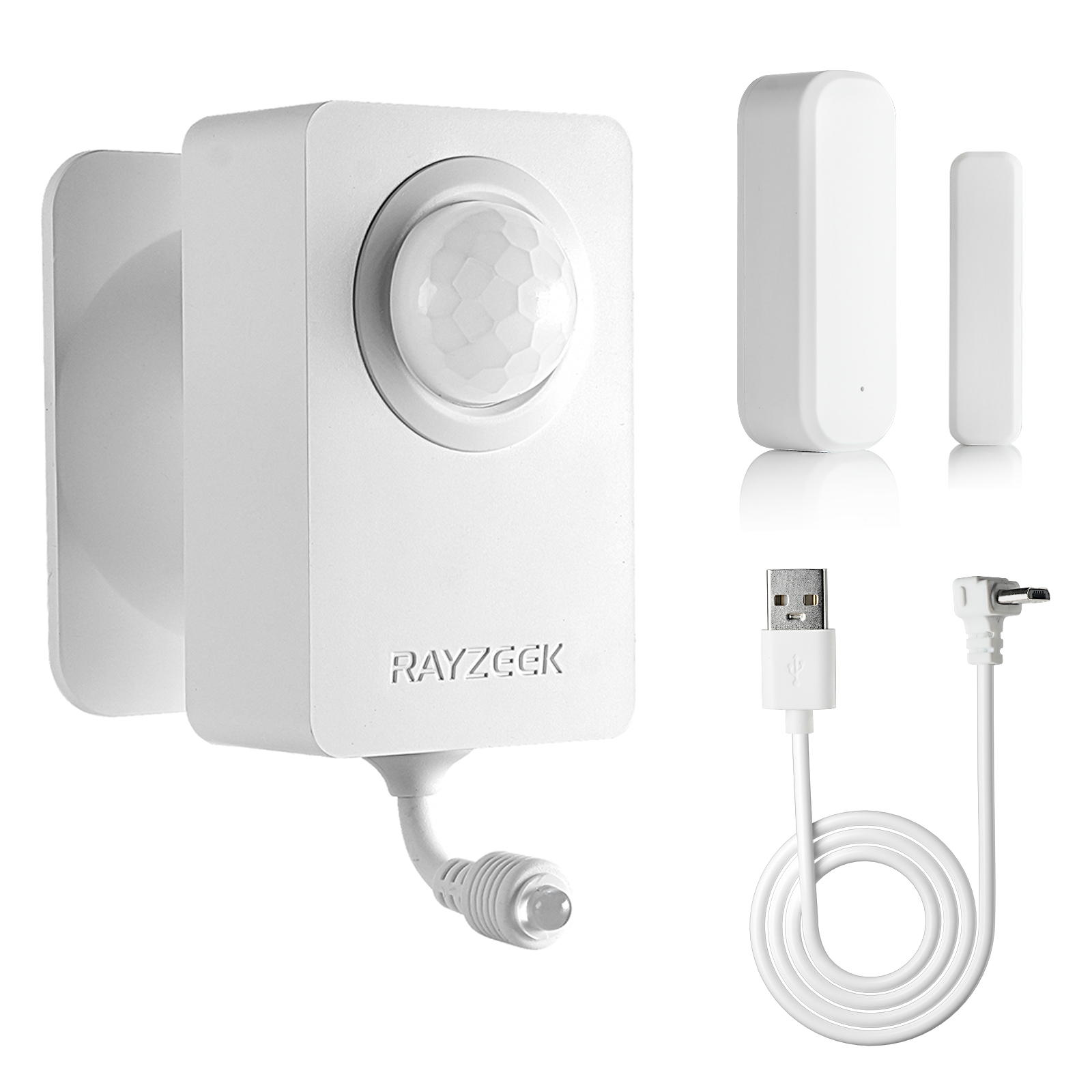
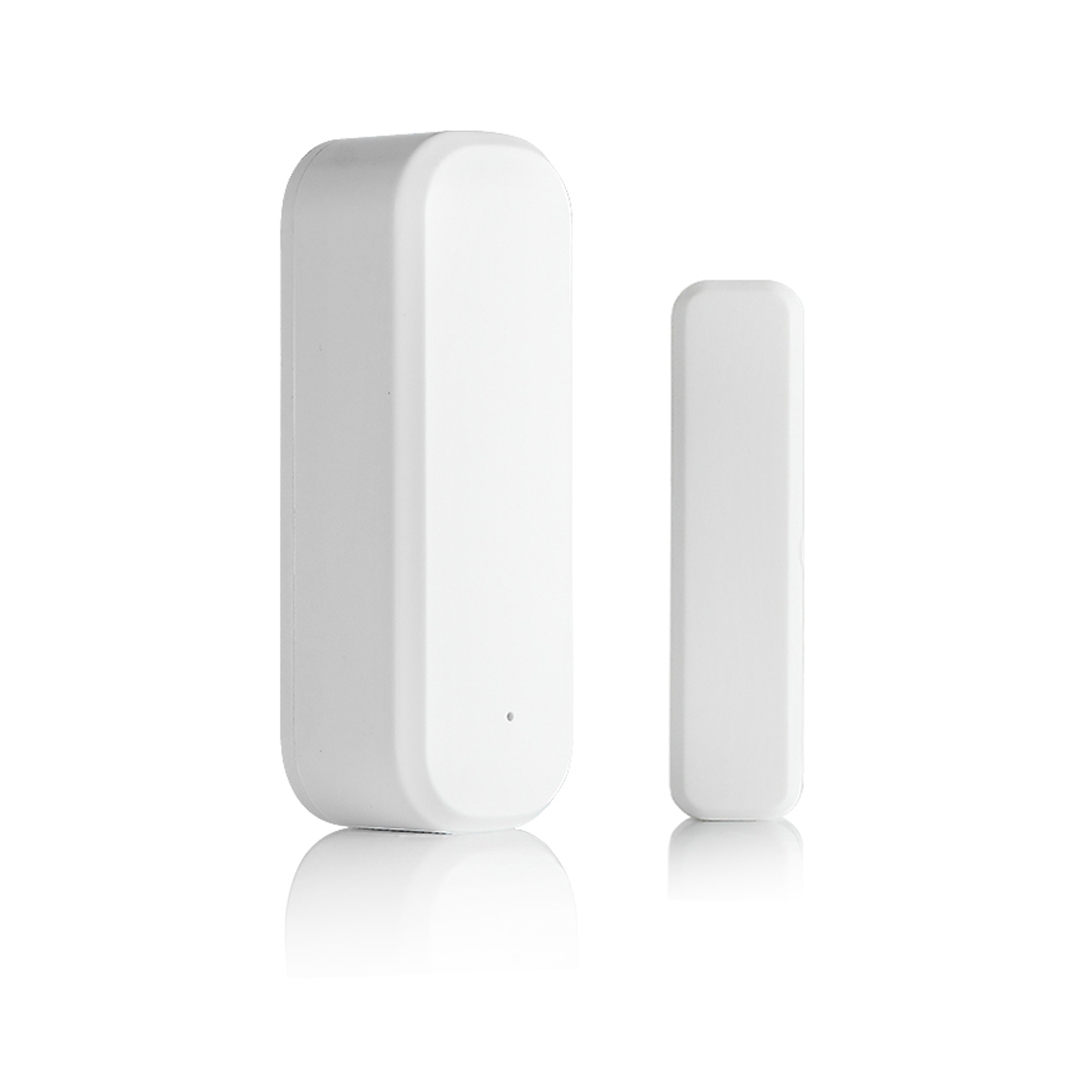
- Wireless motion sensor
- Hardwired control
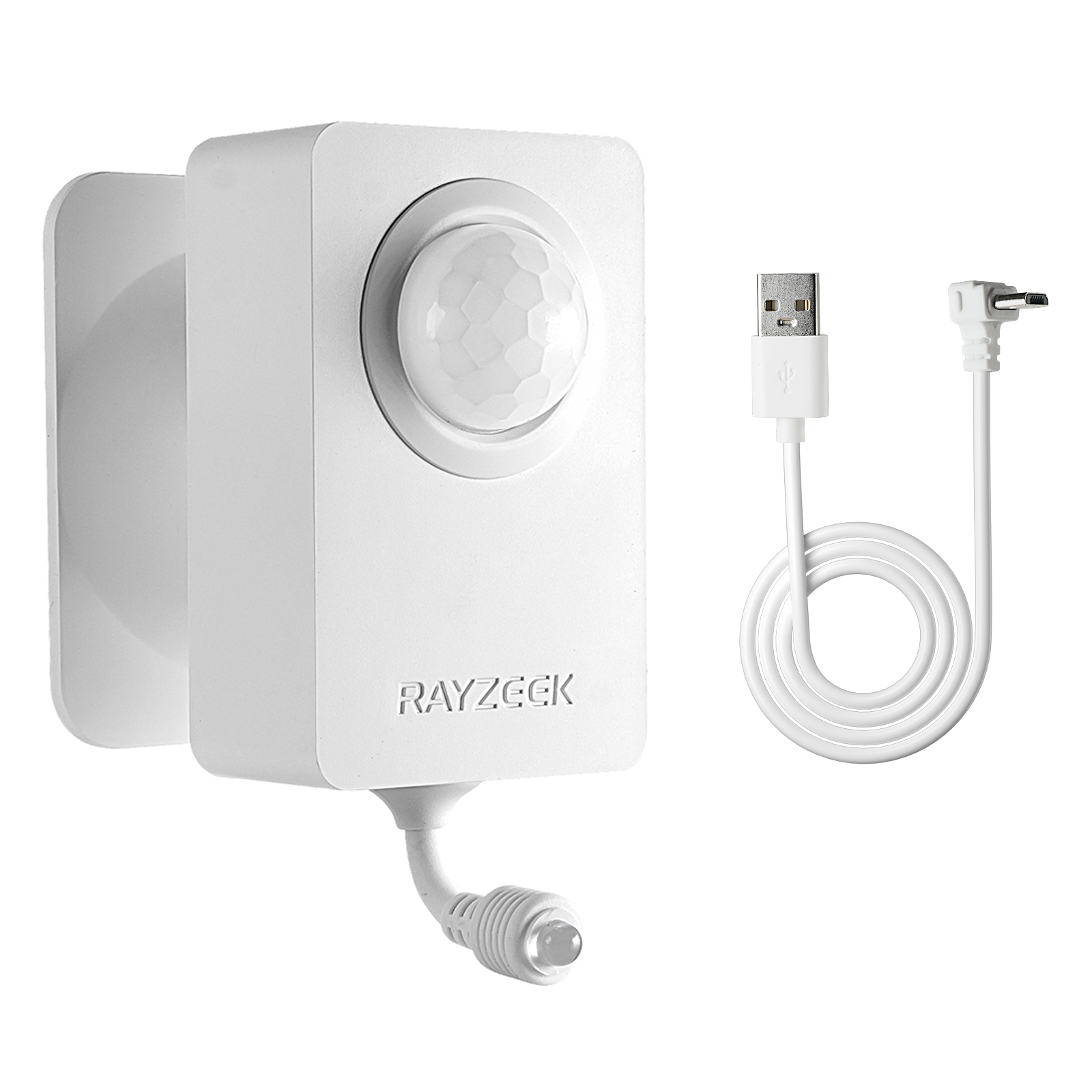
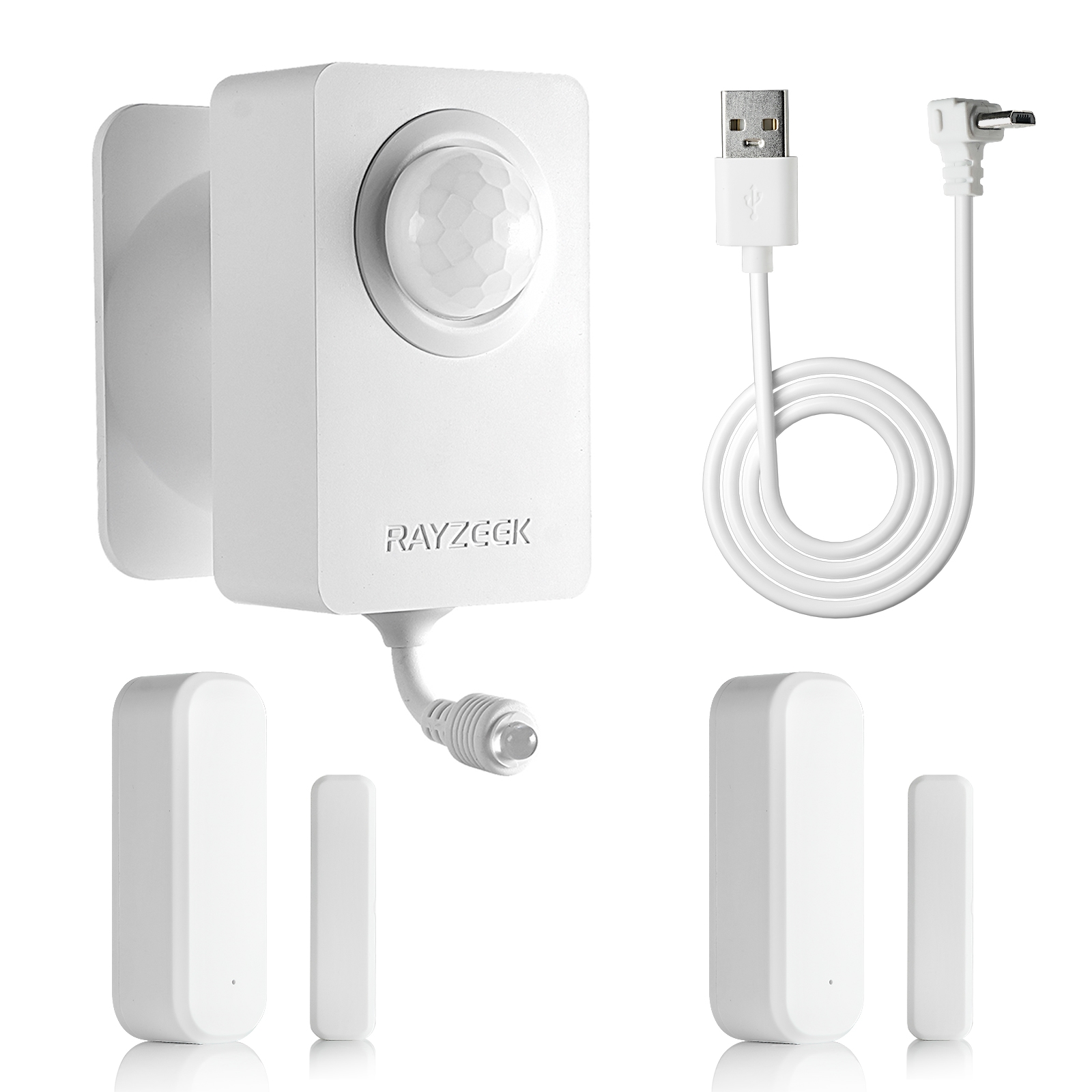
- Voltage: 2x AAA Batteries / 5V DC (Micro USB)
- Day/Night Mode
- Time delay: 15min, 30min, 1h(default), 2h
- 5V DC
- Transmission Distance: up to 30m
- Day/Night mode
- 5V DC
- Transmission Distance: up to 30m
- Day/Night mode
- Voltage: 2 x AAA
- Transmission Distance: 30 m
- Time delay: 5s, 1m, 5m, 10m, 30m
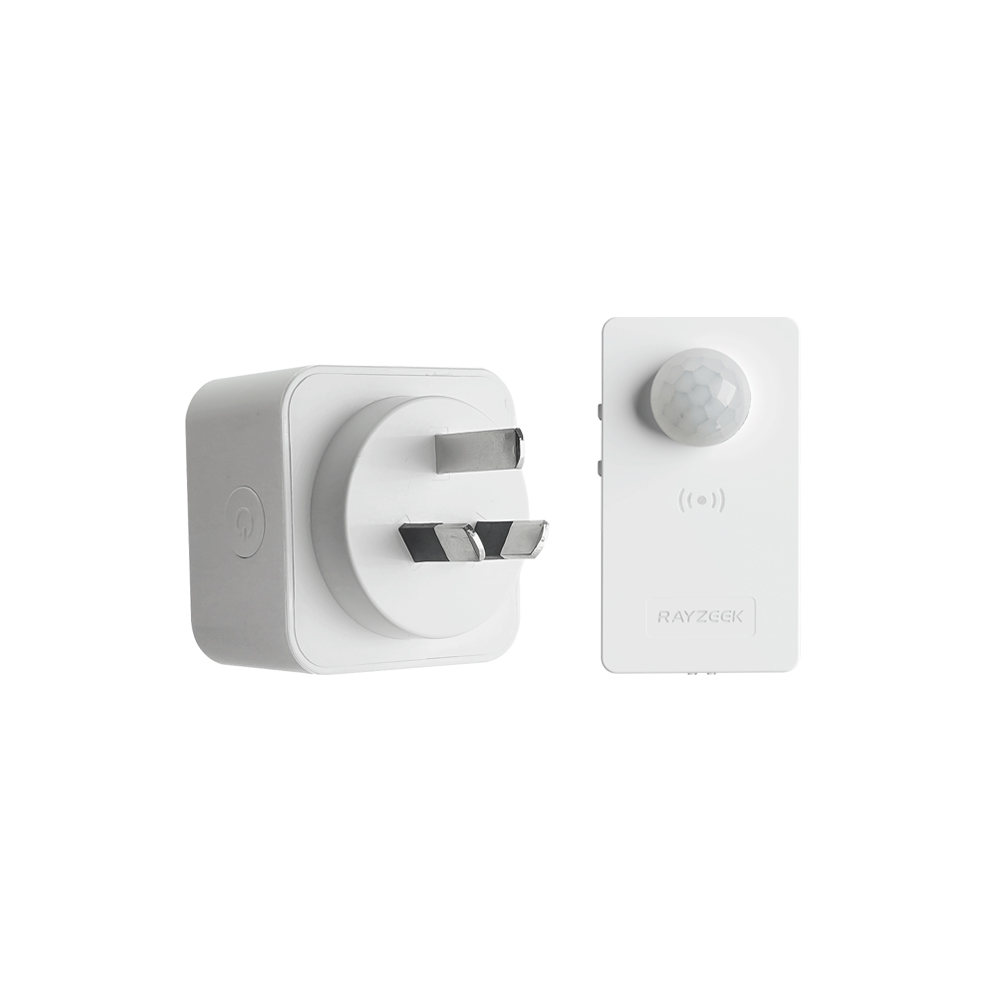
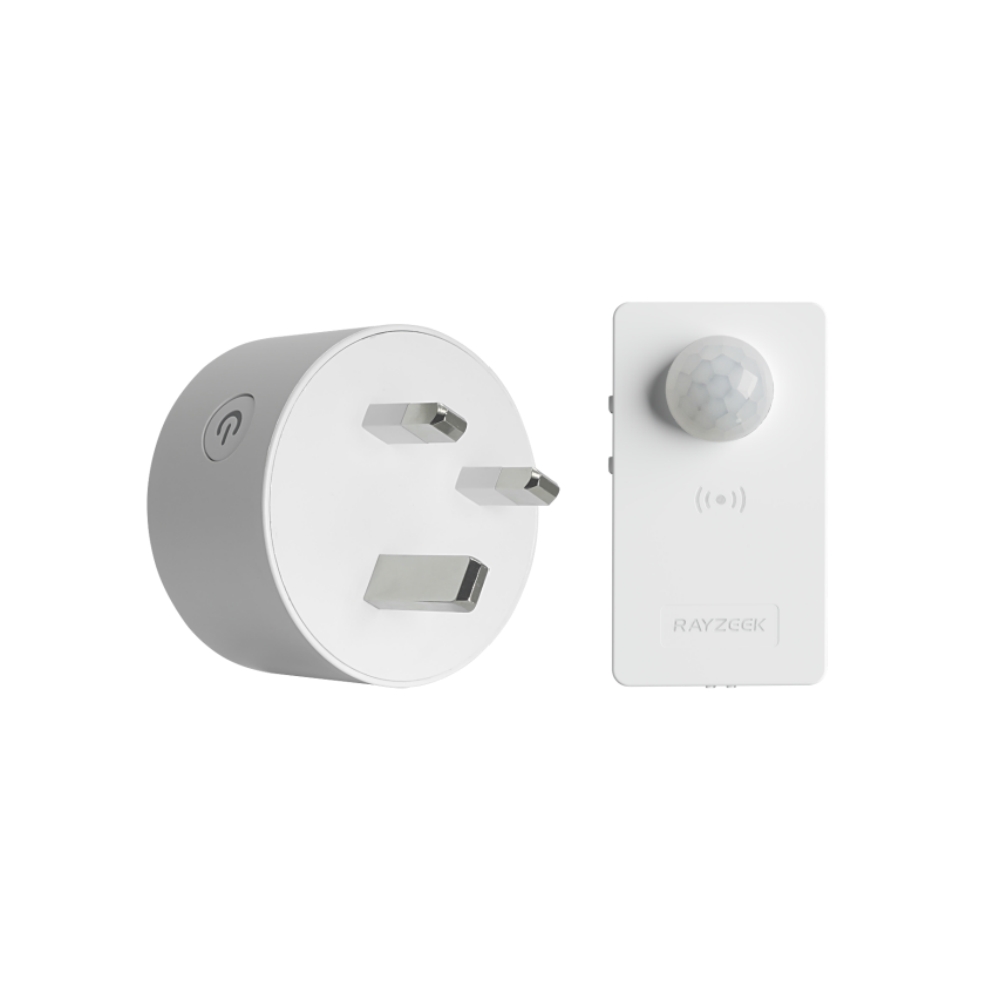
- Load Current: 10A Max
- Auto/Sleep Mode
- Time delay: 90s, 5min, 10min, 30min, 60min
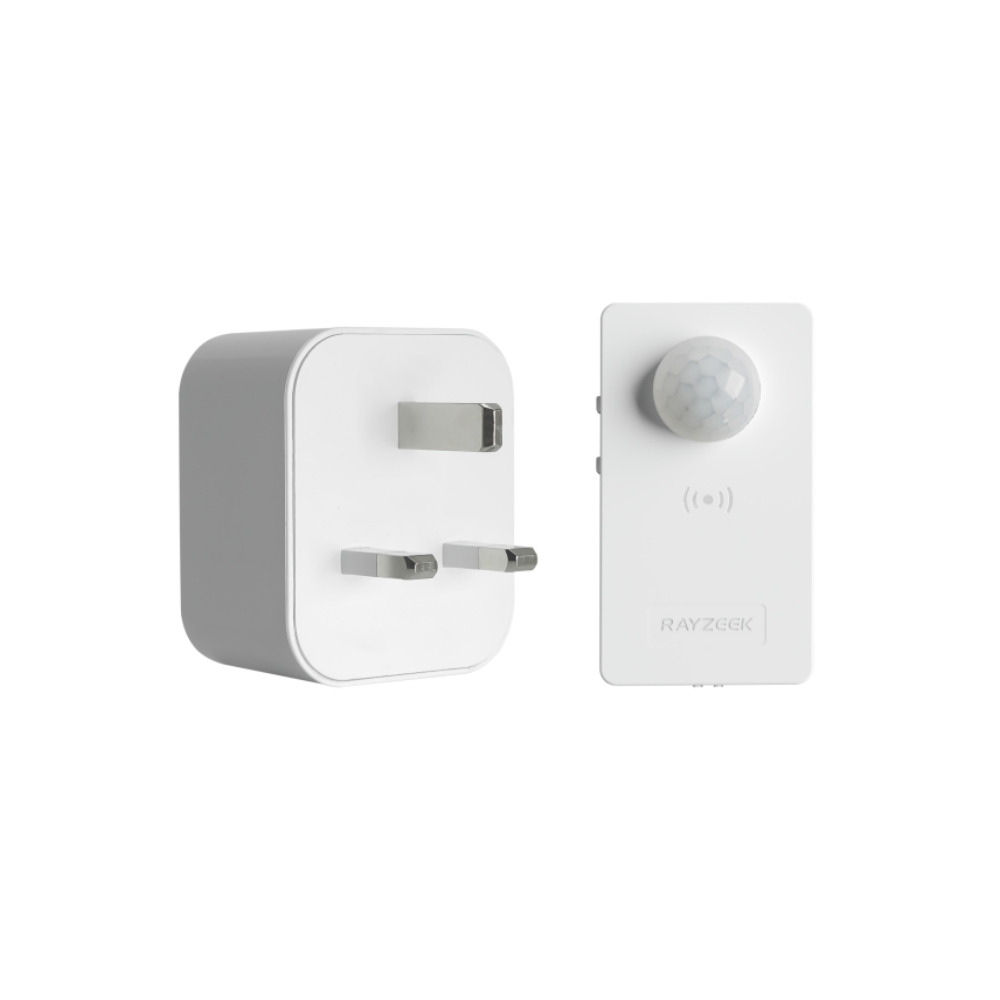
- Load Current: 10A Max
- Auto/Sleep Mode
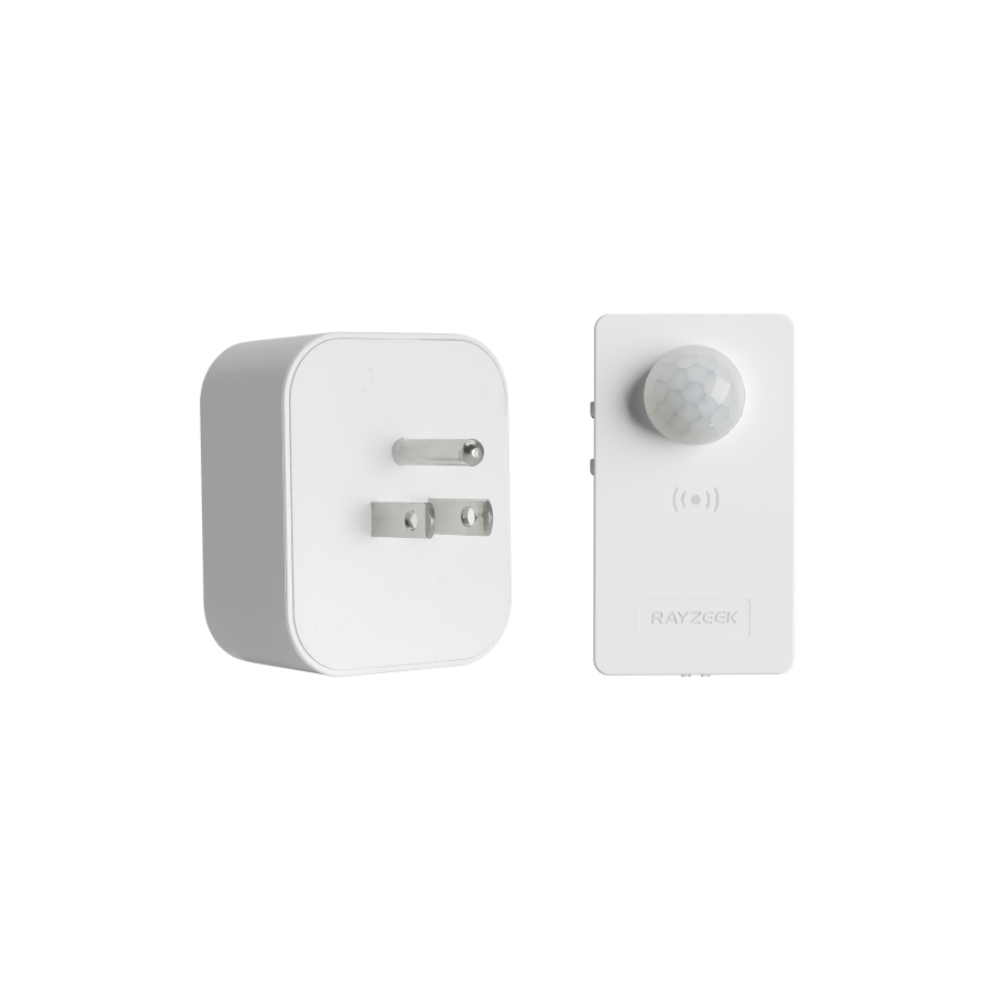
- Time delay: 90s, 5min, 10min, 30min, 60min
- Load Current: 10A Max
- Auto/Sleep Mode
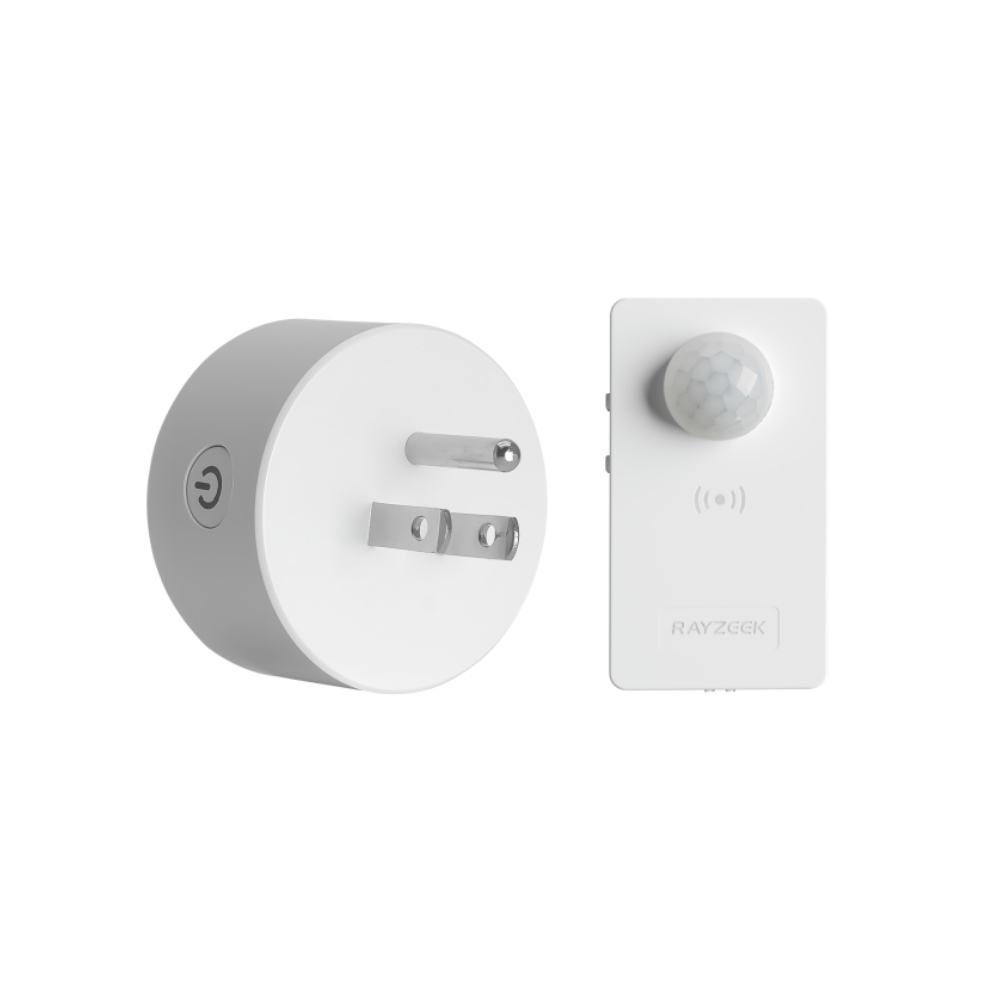
- Time delay: 90s, 5min, 10min, 30min, 60min
- Load Current: 10A Max
- Auto/Sleep Mode
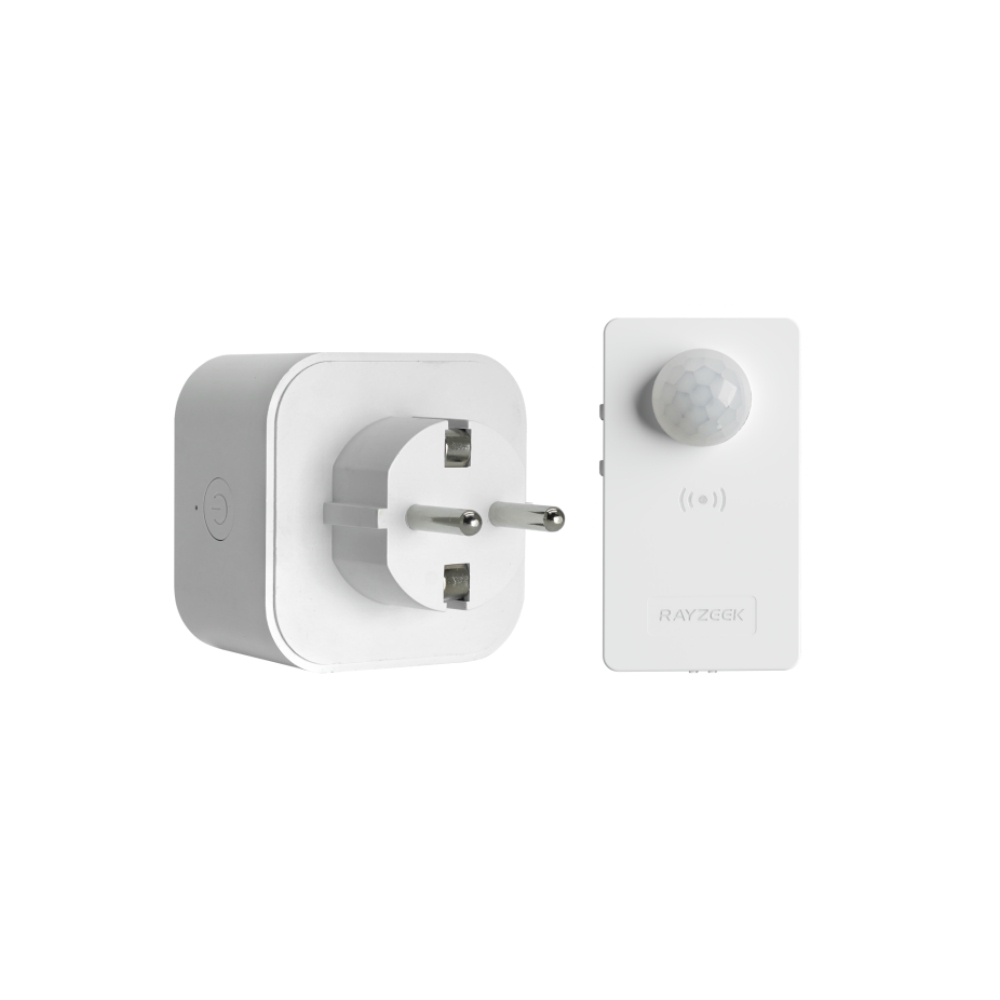
- Time delay: 90s, 5min, 10min, 30min, 60min
- Load Current: 10A Max
- Auto/Sleep Mode
- Time delay: 90s, 5min, 10min, 30min, 60min
- Load Current: 10A Max
- Auto/Sleep Mode
- Time delay: 90s, 5min, 10min, 30min, 60min
- Occupancy mode
- 100V ~ 265V, 5A
- Neutral Wire Required
- 1600 sq ft
- Voltage: DC 12v/24v
- Mode: Auto/ON/OFF
- Time Delay: 15s~900s
- Dimming: 20%~100%
- Occupancy, Vacancy, ON/OFF mode
- 100~265V, 5A
- Neutral Wire Required
- Fits the UK Square backbox