What is Stray Light
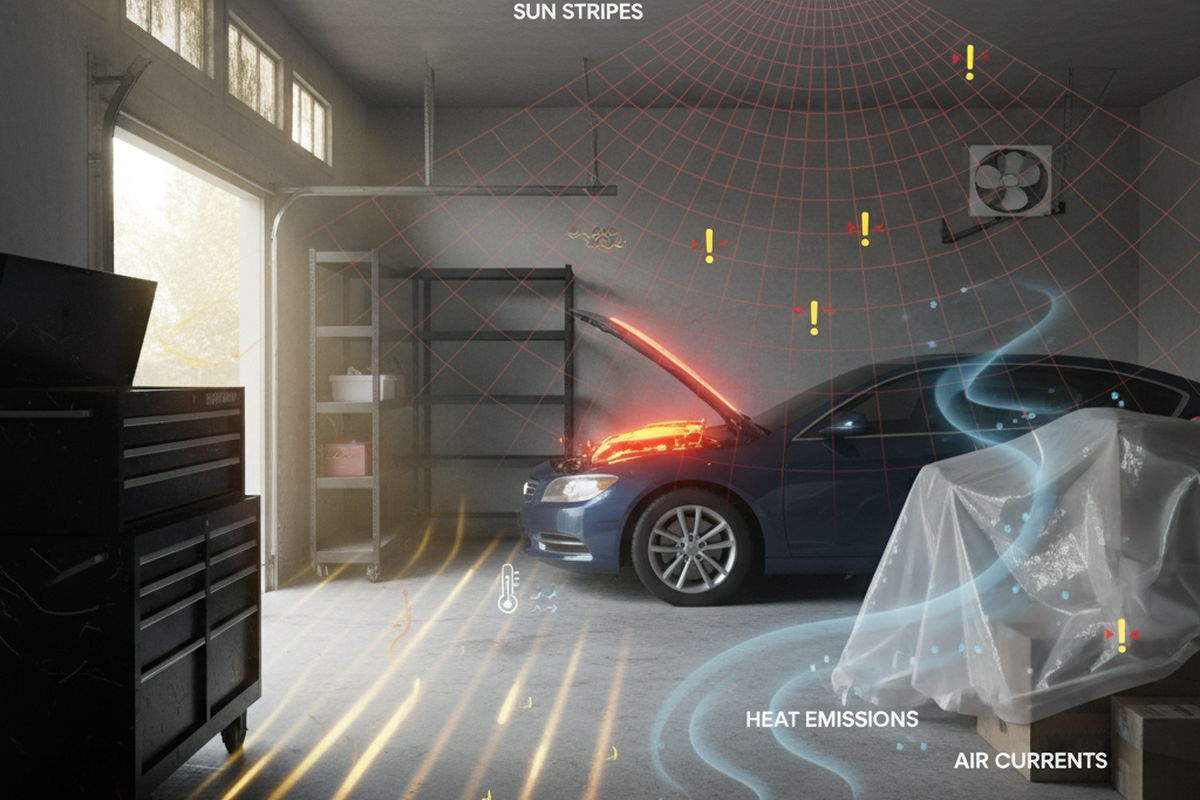
Stray light refers to any unwanted light that enters an optical system and interferes with its intended functions. It can occur in both imaging and projection systems, but it is particularly critical to control in imaging systems. There are several sources of stray light that can affect the performance of an optical system. One common source is light reflections off mechanical mounting surfaces within the system. These reflections can bounce off the surfaces and enter the imaging or projection path, causing unwanted interference.
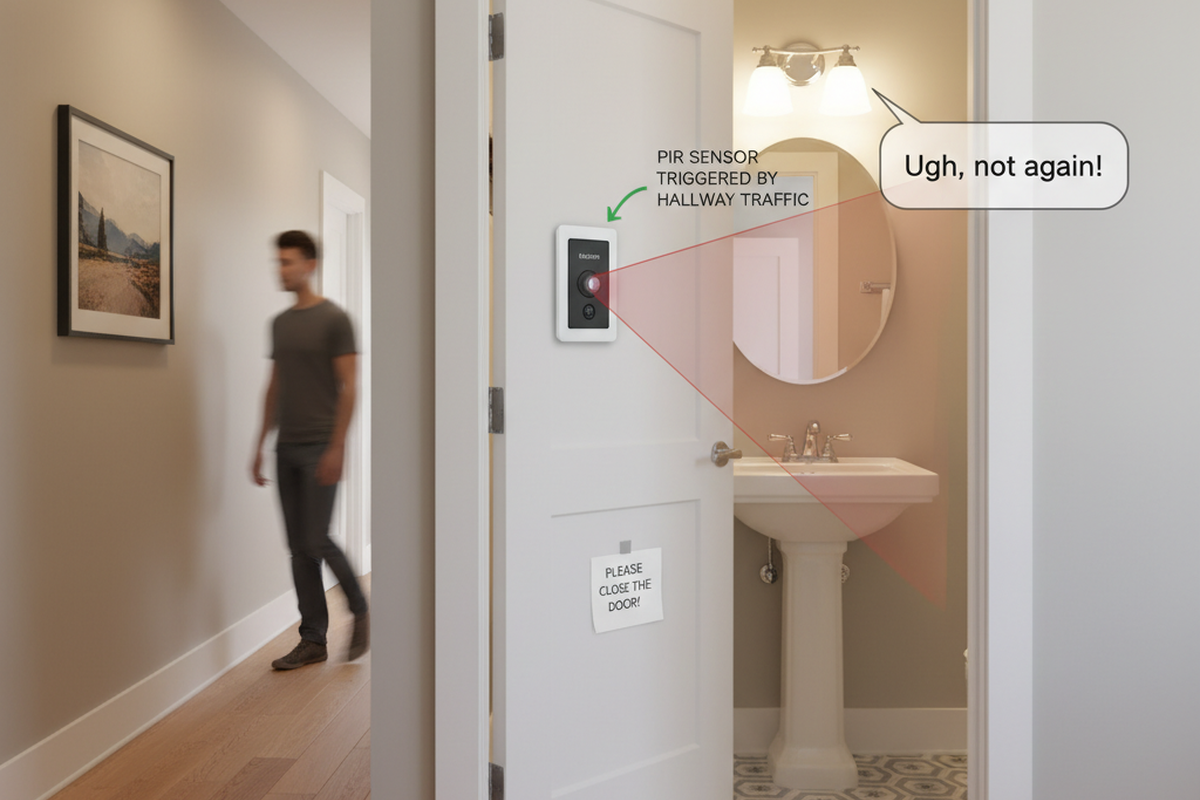
Get Inspired by Rayzeek Motion Sensor Portfolios.
Doesn't find what you want? Don't worry. There are always alternate ways to solve your problems. Maybe one of our portfolios can help.
Another source of stray light is light leakage through gaps or cracks in the system enclosure. If there are any openings in the enclosure, external light can enter the system and interfere with the desired light output. Additionally, stray light can result from light scattering off dust particles or imperfections on the system’s optical surfaces. These imperfections can cause light to scatter in unintended directions, leading to unwanted interference in the optical system. Stray light can also originate from internal sources, such as elements of the system emitting light due to their own heat, especially in infrared-sensitive systems. This can introduce unwanted infrared radiation into the system, affecting the accuracy and quality of the imaging or projection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is It Called When You See Glare Around Lights
Seeing halos around lights is a phenomenon known as diffraction. Diffraction occurs when light bends as it enters the eye. While glasses and contact lenses can sometimes cause diffraction, it can also be a side effect of certain diseases.
What Does Stray Light Mean
Definition. Stray light refers to any unwanted electromagnetic radiation that disrupts the intended functions of an optical system.
What Causes Stray Light
Stray light can be caused by various factors, such as imperfections in the dispersing element or other optical surfaces, diffraction effects, optical aberrations, or damaged or worn components. It is also important to ensure that extraneous light, such as light leaks at cell compartments or other mechanical boundaries, is eliminated.
How Do You Determine Stray Light
Stray light in an instrument refers to light that is present in the instrument but does not match the wavelength set on the monochromator. To put it simply, if the monochromator is set to 600 nm, any light that is not exactly 600 nm is considered stray light.
What Is the Stray Light in a Spectrophotometer
In a spectrophotometer, stray light refers to the light that bypasses the sample and directly reaches the detector. This occurrence can cause inaccurate measurement outcomes.
How Can We Prevent Stray Light
Limiting the aperture size: By limiting the size of the aperture, we can effectively prevent stray light from entering the system and affecting the detector. This is particularly crucial in applications that require high-contrast imaging, as even a minor amount of stray light can have a negative impact on the quality of the image.
How Does Stray Light Affect Absorbance
After a brief period of decreasing, the measured absorbances level off as they reach the stray light values for the instrument. Stray light photometric artifacts consistently result in absorbance values that are lower than the actual values.
What Is Stray Light Analysis
In essence, stray light analysis refers to the examination of light that does not follow the intended path within a system and instead affects the quality of the desired image. It is crucial to assess the impact of this stray light on performance before proceeding with physical prototyping.
What Is the Limit of Stray Light in UV
Stray light can pose a challenge across the entire spectral range of a spectrophotometer, encompassing the UV, VIS, and NIR ranges. However, it becomes increasingly problematic as you approach the UV range, specifically within the range of 190-300 nm.