What is Far Red Light
Far red light, also known as FR light, is a waveband at the extreme end of the visible light spectrum, with wavelengths between 700 and 780 nanometers (nm). It falls outside the range of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), which includes wavelengths between 400 and 700 nm. While far red light has traditionally been considered to have minimal input in photosynthesis, recent studies have shown its unique ability to enhance the efficiency of photosynthesis when combined with shorter wavelength light.
Far red light plays a crucial biological role in plant growth and yield. It interacts with shorter wavelength photons to increase the efficiency of photosynthesis, even though its own photosynthetic efficiency decreases with increasing wavelength. By delivering far red light to crops at specific times, growers can manipulate plant responses, accelerate flowering, and increase overall yield. This manipulation is made possible through the utilization of intelligent lighting control systems, which allow growers to leverage the benefits of far red light. It also affects plant growth and the ability of plants to capture light. Plants perceive an increase in the proportion of far-red photons as a signal of shade and respond by growing taller to outcompete neighboring plants. By adjusting the red to far-red ratio in the grow light spectrum, growers can manipulate plant appearance, shape, and height, as well as maximize yield by increasing light capture or enhancing flowering.
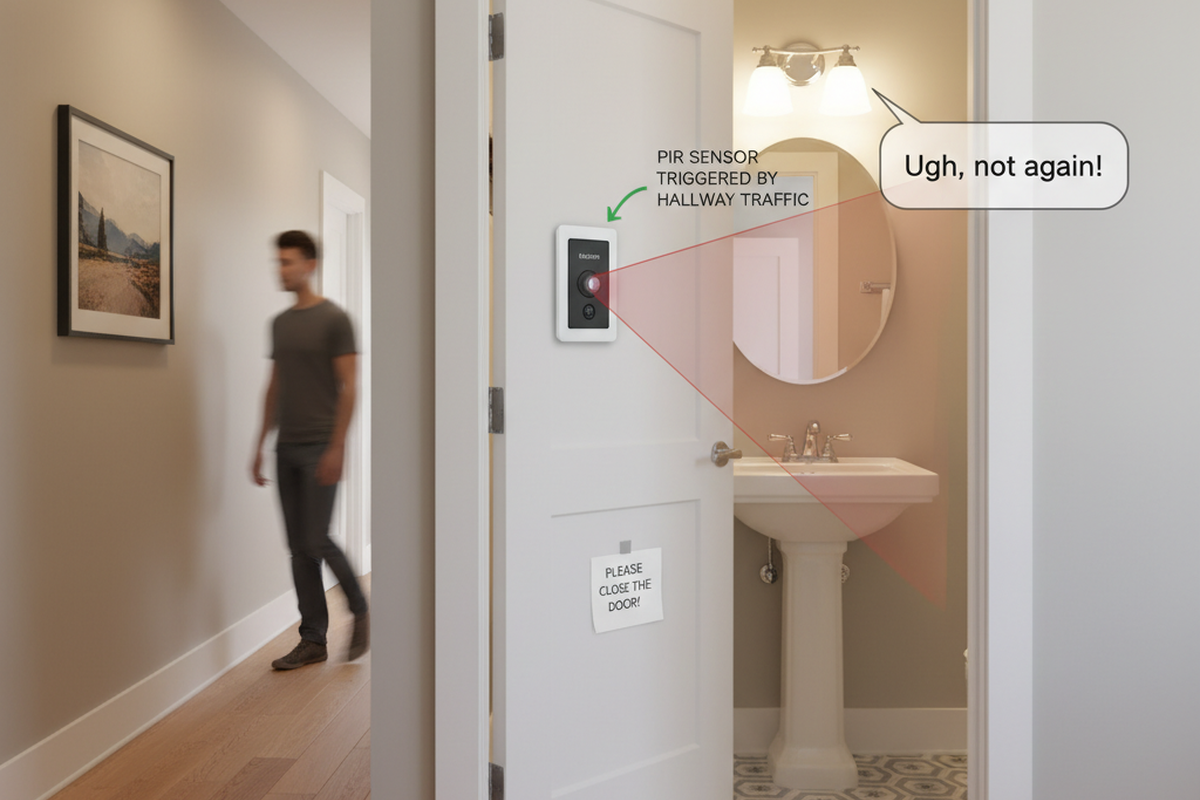
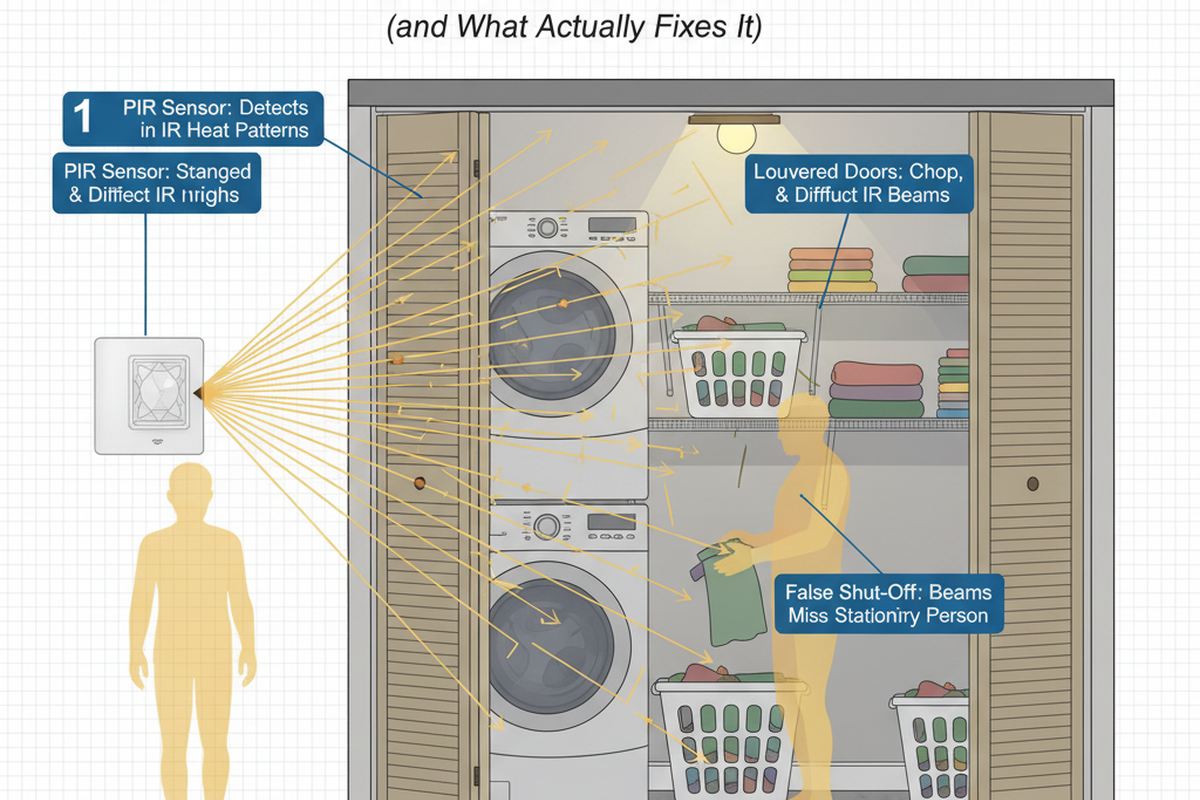
Get Inspired by Rayzeek Motion Sensor Portfolios.
Doesn't find what you want? Don't worry. There are always alternate ways to solve your problems. Maybe one of our portfolios can help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Color Light Is Best for Indoor Plants
Blue light is the optimal choice for indoor plants as it stimulates the production of chlorophyll, which is essential for their growth. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in promoting germination and root development in young plants and seedlings. On the other hand, red light is responsible for regulating plant growth and facilitating the production of flowers and fruit.
What Does Far-Red Light Do
Far-red light has a significant impact on extension growth, which refers to the size of leaves, the length of stems, and ultimately the height of plants.
What Is Difference Between Red Light and Far-Red Light
Red light is typically defined as light with a wavelength ranging from 600 to 700 nm. On the other hand, far-red light, which marks the beginning of the infrared spectrum, has a wavelength between 700 and 800 nm.
What Does Far-Red Light Do for Plants
Adding far-red light to plants, which consists of photons with wavelengths ranging from 700-750 nanometers (nm), can enhance the photosynthetic rate by enabling plants to utilize light more effectively in the production of carbohydrates.
What Is the Difference Between Deep Red and Far-Red
Deep red, also known as photo red in certain consumer brands, has a wavelength of approximately 660-670 nm. On the other hand, far red, primarily utilized for plant cultivation purposes, has a wavelength of around 730 nm, which is situated at the threshold of human visual perception.
What Does Far Red Light Look Like
Far-red light is a segment of light that is found at the far end of the red section of the visible spectrum, right before infrared light. Typically, it is considered to be within the wavelength range of 700 to 750 nm and can be faintly perceived by the human eye.
What Absorbs Far Red Light
Phytochrome, a pigment, is responsible for absorbing both red light and far-red light.
Is Far-Red Light the Same as Infrared
With a wavelength range of 700-850 nm, far-red light is situated between red light and infrared light.
Is There More Far-Red Light at Night
As the day transitions into night, the proportion of far-red light surpasses that of red light. This shift in light spectrum leads to an increase in the levels of Pr, resulting in a slightly higher concentration of Pfr and a lower concentration of Pr. During the dark period, plants naturally produce Pr, which accumulates over time.
Can Plants Get Too Much Red Light
Many plants that are cultivated solely under red light, such as those grown indoors using only red LEDs, tend to exhibit elongated growth patterns. The leaves become thin and large, causing the plants to grow tall. However, it is important to note that plants grown exclusively under red light often do not exhibit desirable growth characteristics.