What is Filament
Filament is the thin wire or coil found inside a light bulb that emits light when heated. Typically made of tungsten, which has a high melting temperature, the filament is the main component that enables incandescent lamps to produce visible light.
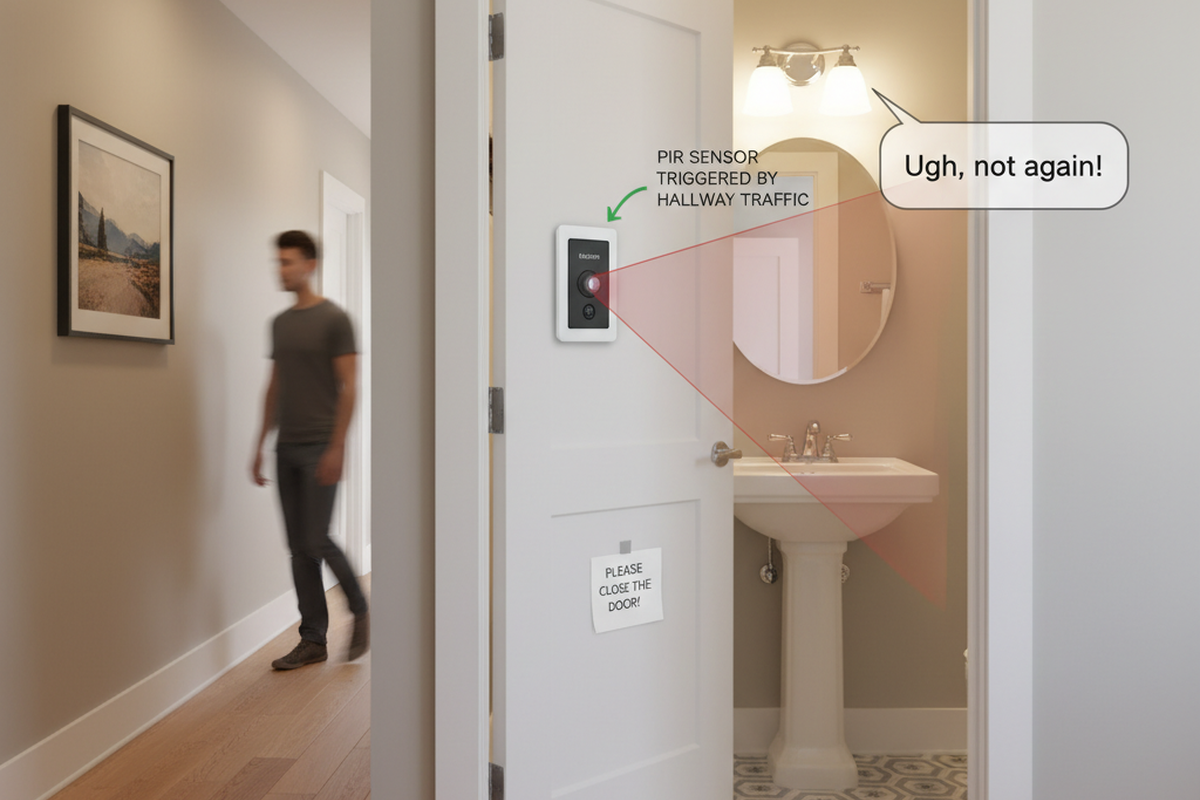
Looking For Motion-Activated Energy-Saving Solutions?
Contact us for complete PIR motion sensors, motion-activated energy-saving products, motion sensor switches, and Occupancy/Vacancy commercial solutions.
To prevent combustion, the filament is housed in a sealed, oxygen-free chamber. In the early days of light bulbs, the air was removed to create a near vacuum, but this caused the tungsten atoms to evaporate, leading to a shortened lifespan of the bulb. To address this issue, modern light bulbs now use inert gases, such as argon, to reduce the loss of tungsten atoms. When a tungsten atom evaporates, it is likely to collide with an argon atom and bounce back towards the filament, rejoining the solid structure. This prevents the elements from combining in a combustion reaction.
Incandescent light bulbs, which rely on filaments, are not as energy-efficient as other lighting technologies. They waste a significant amount of energy by emitting most of it in the form of heat-carrying infrared light photons, with only about 10 percent of the light falling within the visible spectrum. As a result, incandescent bulbs have been gradually replaced by more advanced and energy-efficient alternatives like fluorescent lamps and LEDs.
Get Inspired by Rayzeek Motion Sensor Portfolios.
Doesn't find what you want? Don't worry. There are always alternate ways to solve your problems. Maybe one of our portfolios can help.